The budgie, native to Australia, was first scientifically described in 1805. Over the 19th century, these birds were brought to Europe and the US, leading to widespread popularity and captive breeding. With advancements in breeding techniques, a multitude of budgie varieties have emerged from the 1920s to the present day.
Where Do Budgies First Come From? The origin of budgies is a journey that takes us thousands of miles away to the hot, sun-soaked plains and eucalyptus forests of Australia.
The land down under, with its unique and vibrant biodiversity, is the birthplace of these small, energetic birds.
Budgies, or budgerigars as they are scientifically known, are native to this large, arid continent and have adapted to thrive in its diverse environments.
These captivating birds have been part of the Australian landscape for thousands of years, with Indigenous Australians having known about them long before European explorers first set foot on the continent.
Their presence was an integral part of the complex ecosystem, contributing to the biodiversity that made the Australian wilderness so distinctive.
In their native Australian environment, budgies formed large flocks and traversed the expansive landscapes in search of food and water.
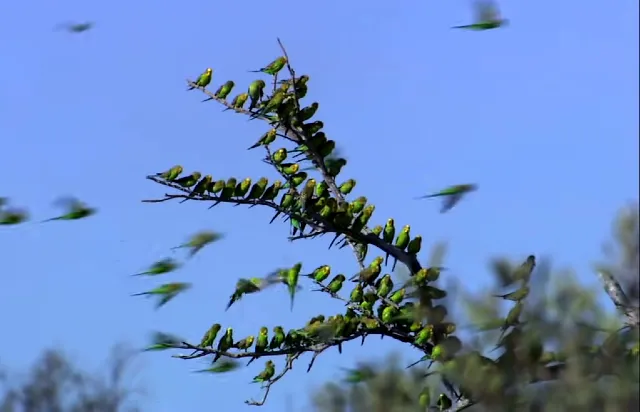

It’s a testament to their tenacity and adaptability that they were able to thrive in such challenging conditions.
Their predominantly green plumage, evolved as an effective camouflage, blending seamlessly with the lush vegetation of their surroundings.
The budgie’s journey from the wilderness of Australia to homes across the globe is a testament to their appealing characteristics.
With their vibrant colors, cheerful demeanor, and ability to mimic human speech, budgies have become one of the most beloved pet birds in the world.
Yet, even though they’ve found their way into countless homes across continents, their roots remain firmly in the Australian outback.
The History Of The Budgies By Important Periods
1805: George Shaw And Frederick Polydore Nodder’s Scientific Description
The year 1805 marks a significant milestone in the history of budgies, thanks to the efforts of English botanist George Shaw and illustrator Frederick Polydore Nodder.
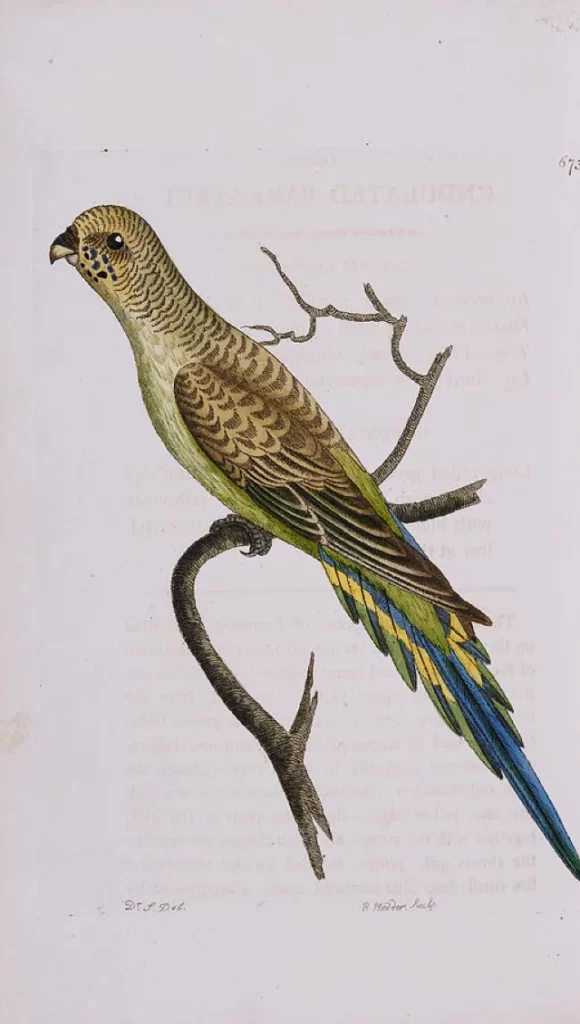

They brought the budgie, native to the vast landscapes of Australia, into the scientific spotlight.
Fascinated by the bird’s vivid plumage and spirited nature, Shaw took on the task of providing a thorough scientific description.
This process, enhanced by Nodder’s precise illustrations, culminated in the formal classification of the budgie under the name Melopsittacus undulatus, meaning ‘melodious parrot with wavy lines’.
This endeavor not only introduced the budgie to Western science but also sparked widespread interest in this vibrant creature, setting the stage for its global popularity.
1830s-1840s: Arrival In Europe
During the 1830s and 1840s, Europe witnessed the arrival of a tiny avian guest from Australia – the budgie.
Its introduction into the continent brought about a wave of fascination, thanks largely to the bird’s vibrant colors, charismatic personality, and capability to mimic human speech.
The European populace, from the nobility to commoners, embraced these exotic newcomers with open arms, leading to a surge in their popularity.
The ensuing years saw the establishment of numerous breeding programs across the continent, paving the way for the budgie’s continued presence and popularity in European households to this day.
1840s: First Captive Breeding In Europe
The 1840s marked another pivotal moment in budgie history with the commencement of the first captive breeding programs in Europe.
The initial success of the bird’s introduction led to a heightened demand for these colorful companions.
To meet this demand, aviculturists embarked on the journey of breeding budgies within a controlled environment.
The practice not only helped ensure a sustainable population of budgies in Europe, separate from their native Australia, but also opened up opportunities for studying their behavior, lifespan, dietary needs, and breeding patterns in closer detail.
This decade set the precedent for domestic budgie breeding, and its impact reverberates even today in the many homes across the world that host these delightful birds.
1850s-1860s: Introduction To The United States
Between the 1850s and 1860s, the shores of the United States first welcomed the vibrant presence of budgies.
As Europe was already deeply enamored by these colorful parakeets, it didn’t take long for the fascination to cross the Atlantic.
The Americans, intrigued by the budgie’s lively nature, striking colors, and uncanny ability to mimic human speech, quickly embraced these Australian natives as household pets.
The budgie’s introduction during this period sparked a wave of interest, resulting in their widespread domestication across the country and cementing their status as a favored pet in the American household.
1894: W. Watmough’s Large-scale Breeding Operation
1894 saw a groundbreaking development in the history of budgie breeding with the establishment of W.
Watmough’s large-scale breeding operation.
Watmough, a British aviculturist, recognized the potential in budgies as popular household pets and made a decisive move to industrialize their breeding.
His large-scale operation significantly boosted the availability of these birds outside their native Australian habitat.
It also set a precedent for commercial budgie breeding, demonstrating its viability as a business endeavor.
This leap forward in breeding practices marked a critical step in making budgies accessible and affordable to a broader audience, contributing immensely to their worldwide popularity.
1920s: Emergence Of Color Mutations
The 1920s ushered in a new era of fascination in the world of budgies with the emergence of color mutations.
Until this point, the common budgie sported the natural green plumage of its Australian ancestors.
However, breeding practices led to the unexpected yet captivating discovery of budgies with different colorings.
The first such variation was the blue budgie, an enchanting departure from the traditional green.
This genetic mutation was not just a novelty; it represented the potential for even more diverse budgie colors.
As these vibrant new variants began to appear in pet shops and homes, they added a fresh allure to the already popular budgie, rekindling public interest and adding a new chapter to the budgie’s captivating tale.
1930s-1940s: Popularity In The United States
The 1930s and 1940s witnessed a surge in the budgie’s popularity within the United States.
Following their introduction in the mid-19th century, budgies had gradually woven themselves into the fabric of American pet culture.
But it was during these two decades that the nation truly fell in love with these colorful, chatty companions.
The newfound variety in budgie colors, thanks to the emergence of genetic mutations, added to their appeal.
From East Coast to West Coast, in both urban and rural homes, the budgie became a beloved pet, praised for its vibrant personality and interactive nature.
This period solidified the budgie’s status in the U.S., a popularity that remains steadfast even today.
1950s-1960s: Development Of The “English Budgie”
In the 1950s and 1960s, a unique strain of budgie began to make its appearance, known as the “English Budgie”.

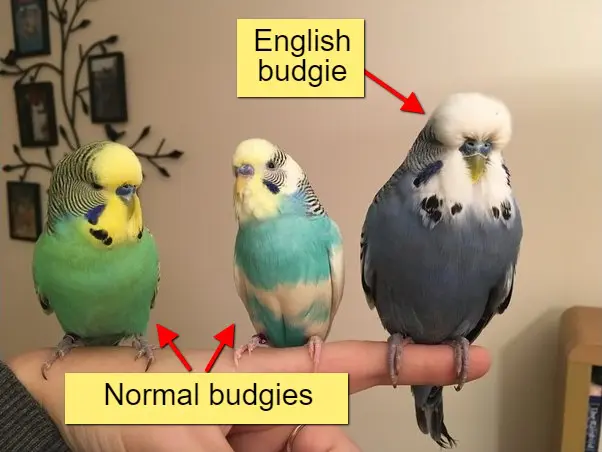
This variety was the result of targeted breeding efforts within the United Kingdom, aimed at developing a budgie with specific characteristics.
The English Budgie, larger in size with a distinctive posture and grander head, quickly became a symbol of refined aviculture.
It was not merely a physical variation but a demonstration of the potential to influence a species’ traits through selective breeding.
This period of innovation within the world of budgies highlighted the growing fascination with these creatures, pushing the boundaries of their genetic diversity and bringing yet another dimension to our relationship with these wonderful birds.
1966: The Budgerigar Society Of New Zealand
1966 was a noteworthy year for budgie enthusiasts in New Zealand as it saw the establishment of The Budgerigar Society of New Zealand.
This organization was created with the mission of promoting the breeding, improvement, and appreciation of budgerigars.
The Society provided a platform for enthusiasts to share knowledge, foster a sense of community, and work towards conserving and enhancing the diverse genetic traits of budgies.
With activities ranging from hosting exhibitions to providing educational resources, the Society played a key role in fostering the continued popularity and responsible breeding of budgies within New Zealand.
Its establishment signified the global appreciation for budgies, acknowledging them as more than just pets, but as a shared passion bringing communities together.
1980s: Global Popularity
By the 1980s, the budgie had truly achieved global popularity.
These small, vibrant birds had made their way into homes across continents, from Australia, their native land, to Europe, the United States, and beyond.
The constant evolution and diversity in their colors and varieties, coupled with their endearing ability to mimic human speech and form bonds with their owners, had made them a household favorite worldwide.
Their popularity was further buoyed by their relatively low maintenance needs and adaptability to various climates.
This period saw the budgie not just as a widely accepted pet but as a global symbol of the joy and companionship that pet ownership can bring.
1990s-present: Evolution Of Mutations And Varieties
From the 1990s to the present day, the world of budgies has seen a continuous evolution in terms of mutations and varieties.
Advanced breeding techniques and a deeper understanding of budgie genetics have resulted in a multitude of color and pattern variations that were unimaginable in the species’ early days.
From opaline and spangled budgies to an array of colors that include violet, yellowface, and cinnamon, the modern budgie palette is a testament to the marvels of genetic diversity.
These advancements have further amplified the budgie’s appeal, offering pet owners a range of choices in terms of appearance while maintaining the delightful personality traits that have endeared budgies to people for more than two centuries.
What Are The Known Budgie Species From 1805 To The Present?
When exploring the known budgie species from 1805 to the present day, one must remember that the term “species” refers to a distinct group within the animal kingdom that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring.
By that definition, the budgie, or budgerigar, is a single species, scientifically known as Melopsittacus undulatus.
This doesn’t mean, however, that all budgies are the same.
Over the years, through natural variation and focused breeding efforts, a multitude of budgie varieties have come into existence.
While they all belong to the same species, these varieties can differ greatly in terms of size, appearance, and behavior.
Two particularly notable budgie varieties are the Australian Budgie, which is the wild, naturally occurring form, and the English Budgie, which has been selectively bred for specific traits.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the characteristics that distinguish these two main budgie varieties.
Australian Budgies (Native Budgies)
The Australian Budgies, also known as the native budgies, are the original species from which all other budgie species have been derived.
These birds are smaller than most of their domesticated counterparts and sport a lively green plumage.
English Budgies (First Domesticated Budgie Species)
English Budgies were the first domesticated budgie species.
They are larger and more robust than the Australian Budgies, and they come in a wider variety of colors and patterns.
What Are The Known Budgie Mutations, Mutation Combinations and Varieties Today?
Remember that many of these mutations can combine with each other and with different base colors (blue series or green series), resulting in a wide array of unique appearances.
It’s a fascinating world of variation, truly a testament to the wonder of budgie genetics!
Here is the list of all budgerigar combinations, mutations and varieties that we have recorded so far on our petiska.com site is as follows:
Color mutations
- Dark factor mutation
- Light green budgie
- Dark green budgie
- Olive green budgie
- Sky-blue budgie
- Cobalt budgie
- Mauve budgie
- Gray factor mutation
- Gray-green (Gray factor)
- Gray (Gray factor)
- Violet factor mutation
- Single-factor (SF) violet mutation
- Double-factor (DF) violet mutation
- Dilution mutation
- Greywing
- Clearwing
- Full-body greywing
- Dilute
- Yellowface & Goldenface mutations
- Single factor yellowface type 1 mutation
- Double factor yellowface type 1 mutation
- Single factor yellowface type 2 mutation
- Double factor yellowface type 2 mutation
- Single factor goldenface mutation
- Double factor goldenface mutation
- Albino mutation
- Lutino mutation
- Dark factor mutation
Striping pattern mutations
- Opaline mutation
- Spangle mutation
- Single factor spangle mutation
- Double factor spangle mutation
- Cinnamon mutation
Pied mutations
- Recessive pied mutation
- Dominant pied mutation
- The single factor dominant pied mutation
- The double factor dominant pied mutation
- Australian pied mutation
- Clearflight pied mutation
- Dark eyed clear variety
Rare & other mutations
- Crest mutation (Crested budgies)
- Full circular (round) crested (Full crested) budgie
- Half circular (round) crested (Half crested) budgie
- Tufted crested budgie
- Japanese helicopter (hagoromo) mutation
- Fallow mutation
- Saddleback mutation
- Texas clearbody mutation
- Slate mutation
- Anthracite mutation
- Blackface mutation
- Mottled mutation/variety
- Half-sider variety
- Crest mutation (Crested budgies)
Mutation combinations
- Rainbow mutations combination
- Lacewing mutations combination
- Creamino budgies
FAQs About Budgie History
What Were Budgies Originally Called?
In their native land of Australia, budgies were originally known as “budgerigars,” a name derived from the Aboriginal term “Betcherrygah,” which roughly translates to “good bird.” The term “budgie” is simply a shortened, affectionate form of “budgerigar,” adopted primarily by English speakers.
How Did Budgies Become Popular Pets?
Budgies became popular pets for several reasons.
Their vibrant colors and striking patterns, combined with their relatively small size and ease of care, make them ideal for home environments.
But perhaps the most compelling feature is their ability to mimic human speech, a talent that captivated people and sparked widespread interest in these charming birds.
This combination of factors, along with strategic breeding and marketing efforts over the years, has solidified the budgie’s status as one of the most popular pet birds globally.
When Were The First Budgie Color Mutations Discovered?
The first budgie color mutations were discovered in the 1920s, with the appearance of the blue budgie.
Until that point, all budgies had a base color of green, akin to their wild Australian counterparts.
The emergence of the blue budgie signaled the potential for a range of color mutations, a potential that breeders have been exploring ever since.
How Has Budgie Breeding Changed Over The Years?
Initially, budgie breeding was a straightforward affair, with no control over the resulting color or pattern of the chicks.
However, with the discovery of color mutations in the 1920s and the subsequent development of genetic understanding, budgie breeding has become a more controlled and strategic process.
Breeders can now breed for specific traits, such as color, pattern, or size, allowing for a much wider range of budgie varieties than ever before.
What Is The Most Significant Period In Budgie History?
It’s difficult to pinpoint a single most significant period in budgie history as their journey from wild Australian birds to popular global pets spans over two centuries and involves many pivotal moments.
However, the discovery of color mutations in the 1920s could be considered a turning point, as it opened up a whole new world of possibilities for budgie breeding and drastically increased the appeal of these birds to potential owners.
Why Are Budgies Green In Their Natural Environment?
In their natural environment, budgies are predominantly green to blend with the verdant foliage of their habitat.
This green color acts as a camouflage, protecting them from predators.
What Are The Differences Between Parakeets And Budgies?
While the term ‘parakeet’ refers to a broad range of small to medium-sized species of parrot, budgie is a specific member of this group.
Thus, all budgies are parakeets, but not all parakeets are budgies.
Sources:
![What is a fallow budgie? [ALL MUTATIONS & VARIETIES]](https://www.petiska.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/what-is-a-fallow-budgie-all-mutations-varieties-1647686348-400x300.jpg)
![All budgie mutations & colors & varieties +PHOTOS [UPDATED]](https://www.petiska.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/all-budgie-mutations-colors-varieties-photos-updated-1652819367-400x300.jpg)

