Budgie eggs guide provide a glimpse into budgie reproduction. From hormonal changes triggering egg laying to the detailed embryonic development inside the egg, each stage reflects nature’s intricate design.
You can also find out about reproductive behaviors, pregnancy symptoms and ovulation patterns, etc.
Diving into the fascinating world of budgie reproduction, I noticed a demand for a comprehensive guide to understanding budgie eggs.
Based on my experiences as a former budgie owner and extensive readings, I’ve put together a detailed article exploring everything from the egg-laying process, signs of laying, to incubation, hatching, and crucial care tips for budgie eggs and chicks.
This resource, I believe, will prove indispensable to both seasoned and novice budgie owners, helping them foster a supportive environment for their feathered companions.

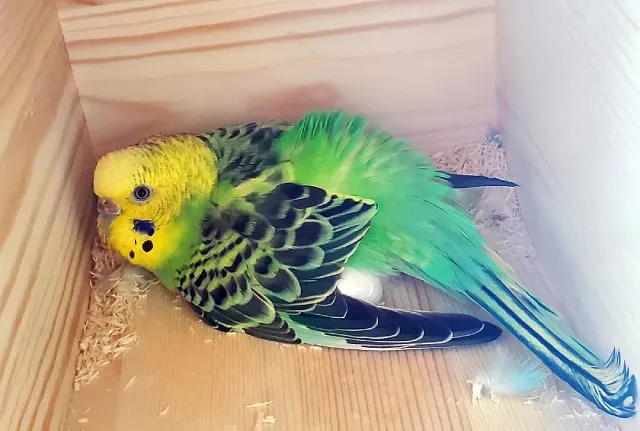
I. Understanding Budgie Egg Laying
Before delving into the complexities of budgie egg laying, it’s important to understand the basics.
Budgies, or parakeets, are small birds that are popular as pets. Their egg laying process involves several stages, each of which is crucial for the survival and growth of their offspring.


How Does the Budgie Egg Laying Process Occur?
The egg laying process in budgies, like in other birds, follows a distinct path:
- Mating: The first step in the process is mating between a male and female budgie.
- Egg Formation: Post-mating, the female’s body begins producing eggs.
- Egg Laying: The female lays her eggs in a nest.
Each of these steps involves distinct physiological changes within the budgie’s body.
What Is Oviposition in Budgies?
Oviposition is a term used to describe the process of egg-laying in animals, including budgies.
It specifically refers to the act of depositing or laying the eggs after they have been formed within the female.
In budgies, oviposition typically takes place in the early morning hours.
How Do Budgies Behave During Egg-Laying?
Budgie behavior changes noticeably during egg-laying. Some common changes include:
- Increased time spent in the nesting area
- Distinctive nesting behavior, such as shredding materials for nest building
- Decreased activity and increased rest periods
What Is the Egg-laying Cycle of Budgies?
The egg-laying cycle in budgies is regulated by various factors, including environmental conditions and the birds’ health.
The typical egg-laying cycle can be outlined as follows:
- Courtship and Mating: This is the pre-laying stage where the budgies mate.
- Egg Laying: The female budgie begins to lay eggs, typically laying one egg every other day.
- Incubation: The female budgie incubates the eggs for about 18-21 days.
- Fledging: Once hatched, the chicks stay in the nest for approximately 30-35 days before they start to fly.
This cycle repeats based on factors such as availability of resources, environmental conditions, and the budgies’ health.
What Are the Clutch Characteristics of Budgies?
A “clutch” refers to the group of eggs laid by a bird during one breeding session.
The characteristics of a budgie’s clutch can provide insights into their reproductive health and behavior.
How Many Eggs Do Budgies Typically Lay in a Clutch?
The number of eggs a budgie lays in a clutch can vary, but typically, a budgie will lay between 4 to 6 eggs per clutch.
However, this can range from as few as 1-2 eggs to as many as 8-10, depending on factors such as the budgie’s age, health, and nutritional status.
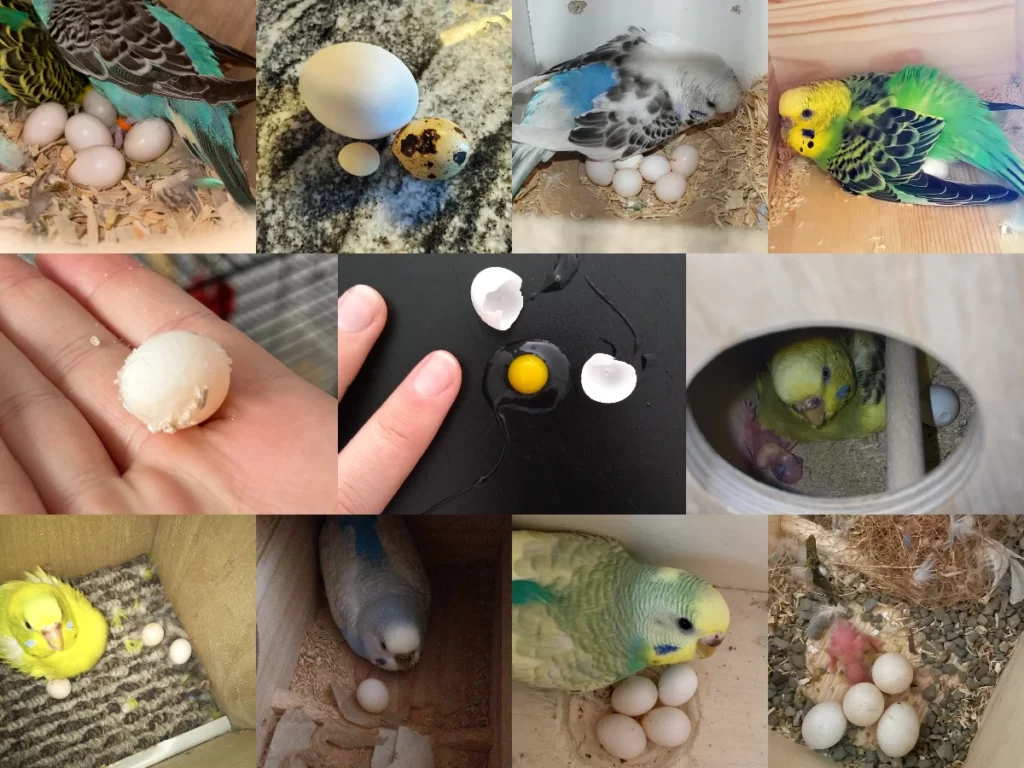
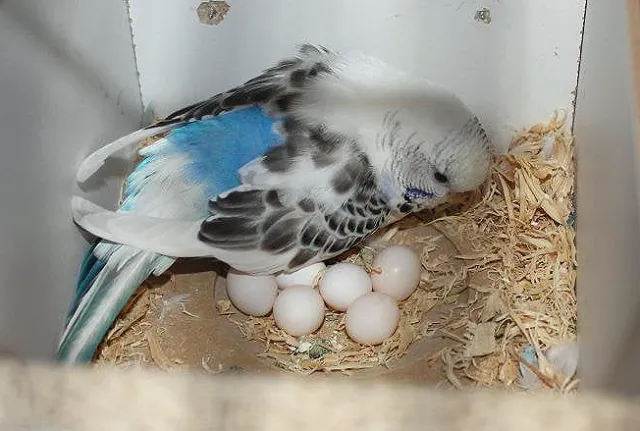
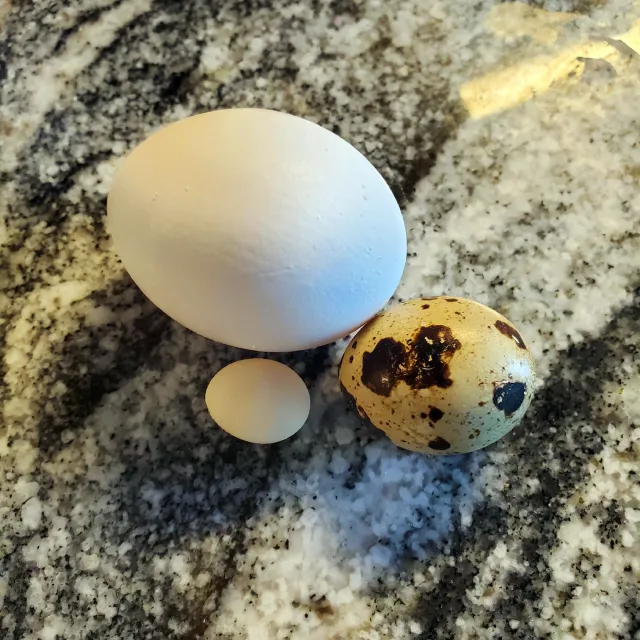
What Do Budgie Eggs Look Like?
As we venture into the topic of budgie eggs, there are several characteristics that you can use to identify them.
- Size and Shape: Budgie eggs typically have an oval shape and are quite small. To give you a clear perspective, they are generally around 1 to 2 centimeters long.
- Shell Texture: The shell of a budgie egg is relatively smooth with a slight sheen.
- Color: The color of budgie eggs can range from white to a slight blue or pale green tint, depending on the budgie.

What Is the Structure of a Budgie Egg’s Shell?
Understanding the structure of a budgie egg’s shell is crucial as it directly impacts the health and development of the budgie chick.
The budgie eggshell consists of:
- An outer layer, known as the cuticle or bloom, that protects the egg from bacterial infection.
- The primary shell body, which is predominantly composed of calcium carbonate crystals.
- An inner layer, known as the shell membranes, provides an extra line of defense against bacterial invasion. It also supports the embryo.
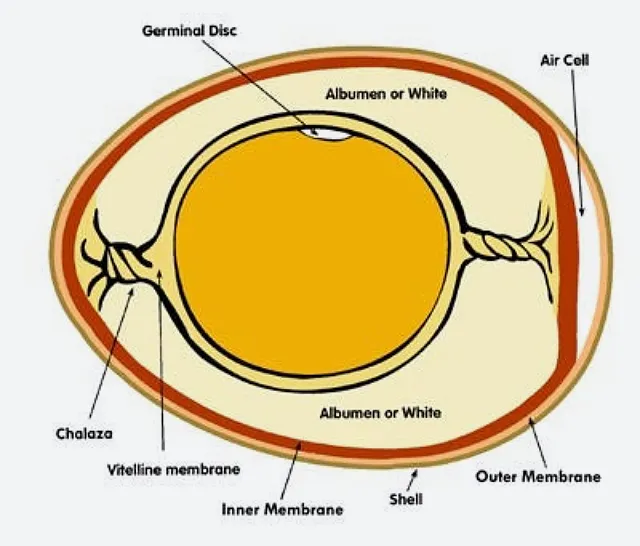
What Color Are Budgie Eggshells?
Budgie eggshells primarily have a white color, but some can present a slight blue or green tint.
This color variance can be attributed to the budgie’s breed and diet.
How Long After Ovulation Does a Budgie Lay Eggs?
The ovulation to egg-laying process in budgies happens relatively quickly. Approximately 24 to 36 hours after the budgie ovulates, she will lay her egg.
How Does Egg Fertilization Occur in Budgies and What Is the Role of a Male Budgie?
Egg fertilization in budgies is an intriguing process. It starts with the copulation of the male and female budgies, where the male budgie transfers his sperm to the female.
Key stages include:
- The male budgie climbs onto the female’s back and aligns his cloaca (reproductive opening) with hers.
- The sperm is transferred from the male to the female budgie.
- The sperm fertilizes the egg as it travels down the female’s oviduct.
The male budgie plays a significant role in the egg fertilization process, but his role doesn’t stop there.
He also helps in nesting and feeding the female during the egg-laying and incubation period.
How Should You Handle Unfertilized Budgie Eggs?
Handling unfertilized budgie eggs requires utmost care. Things to remember include:
- It’s best to leave the eggs in the nest even if they are unfertilized. Removing them can stimulate the female budgie to lay more eggs, potentially leading to health issues.
- If the eggs are unfertilized, the budgies will eventually abandon the eggs after they don’t hatch within the expected time.
How Can You Determine the Viability of Budgie Eggs?
Determining the viability of budgie eggs can be accomplished through a method called budgie egg candling.
This involves shining a light through the egg to observe its contents.
A viable egg typically shows:
- A network of blood vessels around 4-5 days of incubation.
- A dark silhouette with noticeable movement after a week.
Remember, this process requires a delicate touch and should not be done too often as it could harm the developing chick.
II. Signs of Budgie Egg Laying
Signs of egg laying in budgies part of the article is crucial to bird owners because these signs can help determine if your budgie is preparing to lay eggs.
Why Are Budgies Dropping Larger Poop Before Laying Eggs?
One of the first signs you might notice is that your budgie starts dropping larger poop.
But why does this happen?
- Space Requirement: The developing egg takes up space inside the budgie, pushing aside the intestines. This causes larger, less frequent droppings.
- Nutrient Absorption: The budgie’s body absorbs more water from the poop to provide for the growing egg, making the droppings larger and drier.
Unusually large droppings can also be a sign of illness, so it’s important to monitor your budgie’s overall health.
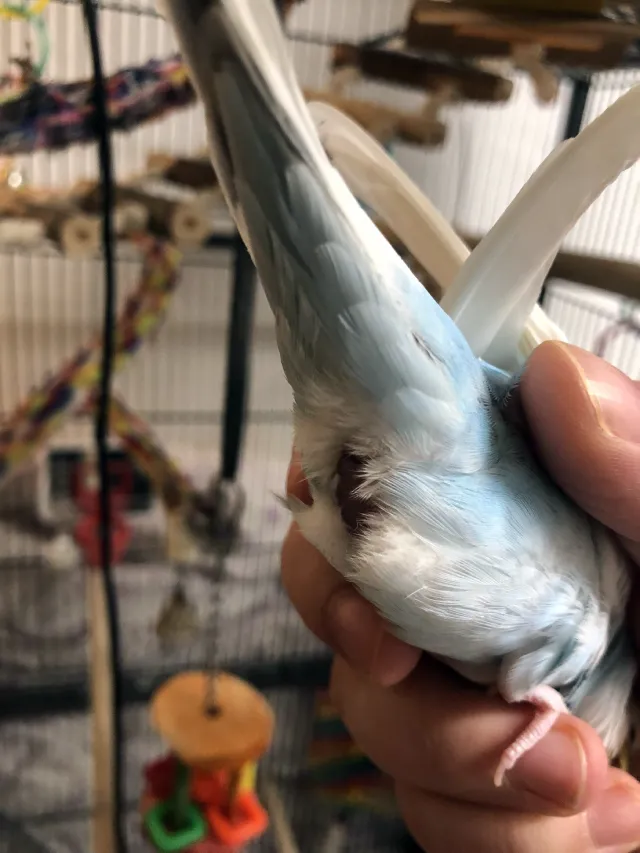
What Does an ‘Egg Bum’ Look Like in Budgies?
An ‘egg bum‘ is another common sign your budgie is preparing to lay eggs.
This refers to a noticeable bulge at the base of the budgie’s abdomen, caused by the presence of an egg.
The egg bum:
- Can be seen when the budgie lifts her tail feathers.
- Causes a more waddling walk.
- May be more noticeable when the budgie is perching.

How Does a Budgie’s Cere Color Change Before Laying Eggs?
The color of the budgie’s cere (the area above the beak) may change as well.
This can be a vital indicator of your budgie’s readiness to lay eggs.
For female budgies:
- The cere color usually darkens and becomes crusty.
- It may turn from light blue or white to a brown or tan color.
What Other Signs Indicate a Budgie Is About to Lay Eggs?
Several other signs can suggest that your budgie is about to lay eggs:
- Increased Appetite: Your budgie may start eating more to gather the energy and nutrients needed for egg production.
- Nesting Behavior: Budgies may start to show nesting behavior such as seeking a secluded spot or shredding paper for a nest.
- Mood Changes: Your budgie might become more territorial or aggressive, which is normal maternal behavior.
What Does Broodiness Mean in Budgies?
Broodiness refers to a behavioral change in budgies when they’re preparing to lay and incubate eggs.
A broody budgie:
- Becomes more territorial.
- Spends more time in the nest box.
- May fluff up her feathers when approached.
Understanding these signs can help you provide the necessary support for your budgie during the egg-laying process, ensuring her health and the successful development of her eggs.
III. Fertility and Budgie Eggs
Budgies are a popular pet and a frequent choice for bird breeding.
Their reproduction process, which involves eggs, is filled with interesting stages, habits, and features, which we’ll unravel in this section.
How Can You Check the Fertility of Budgie Eggs?
Determining whether a budgie egg is fertile or not can be challenging, especially for first-time breeders.
There are, however, methods to do this effectively:
- Egg candling: This is the most common method used to check the fertility of bird eggs, including budgies.
- Weight and color: Fertile eggs are typically heavier than infertile ones and can have a slightly different hue.
What Is Egg Candling in Budgies and How Is It Done?
Egg candling is a non-invasive technique used to check the developmental progress of a bird’s egg.
The term “candling” refers to the method of shining a light source through the egg to observe its contents.
Here’s how it’s done:
- Prepare a bright light source, like a flashlight.
- Darken the room to improve visibility.
- Hold the egg carefully up to the light.
Through this process, you can see the internal contents of the egg.
If the egg is fertile, you will see the embryo developing.
How Can You Test the Fertility of Budgie Eggs?
Beyond candling, the fertility of budgie eggs can be verified through:
- Incubation: Fertile eggs will begin to show development after a few days of incubation.
- Expert verification: A qualified avian veterinarian can test the fertility of the eggs through specialized techniques.
How Can You Understand the Budgie Egg Hatching Chart: The 18-Day Egg Cycle?
Understanding a budgie’s egg cycle is key to successful breeding. Typically, a budgie egg follows an 18-day cycle, which can be broken down as follows:
| Day | Development Stage |
|---|---|
| 1-5 | Early embryonic development |
| 6-8 | First signs of beak, wings, and feet |
| 9-12 | Rapid growth |
| 13-18 | Final growth stage, the chick prepares to hatch |
What Are the Breeding Habits of Budgies? How Do Budgies Reproduce?
Understanding their unique reproductive behaviors is vital for anyone considering breeding these feathered creatures.
Here is an overview of these fascinating habits:
- Mating Season: Budgies do not have a specific breeding season. In the wild, they breed based on the availability of food and water. In captivity, a balanced diet and good care can stimulate breeding throughout the year.
- Nest Preparation: Before the mating process begins, female budgies prepare the nest. They generally prefer cavities or nest boxes for laying eggs.
- Egg Laying: After mating, a female budgie typically lays one egg every other day. A typical clutch consists of four to six eggs.
- Incubation: The female budgie incubates the eggs for about 18 to 20 days before they hatch. During this period, she rarely leaves the nest, relying on the male to bring food.
- Offspring Care: Both parents participate in caring for their chicks. They feed the babies until they fledge (become ready for flight) and become independent.
What Are the Typical Breeding Behaviors in Budgies?
Understanding the typical breeding behaviors of budgies can help owners anticipate and accommodate their needs during this critical period.
Here are the key behaviors to look out for:
- Courtship: Male budgies display various behaviors to attract a mate, including singing, preening, and feeding the female. This often ends with the male and female budgie tapping their beaks together in a ‘kissing’ action.
- Mating: After courtship, the pair will mate. The male climbs onto the female’s back, and they touch their cloaca together. This act is quick but may be repeated several times a day.
- Nesting: The female will begin to spend more time in the nest box and may start to display nesting behavior such as shredding paper or wood shavings for the nest.
How Do Budgies Mate?
Mating in budgies is a straightforward yet fascinating process. Here’s how it happens:
- Courtship Stage: The male budgie woos the female with songs, dances, and feedings. He may also fluff up his feathers to look more attractive.
- Mounting Process: If the female is receptive, she will allow the male to climb onto her back. The male grips the female’s back and balances with his wings.
- Cloacal Contact: The male and female touch their cloacae together, transferring sperm from the male to the female.
- Post-Mating Behavior: After mating, the pair often preen each other and stay close, reinforcing their bond.
IV. Budgie Egg Incubation and Hatching
The process of budgie egg incubation and hatching plays a vital role in the successful breeding of these feathered companions.
What Is the Incubation Period for Budgie Eggs?
The incubation period for budgie eggs generally ranges from 17 to 20 days.
This period can be explained as follows:
- Budgie hens lay one egg approximately every other day until they’ve laid all of their eggs, typically between four and six in total.
- The hen starts incubating the eggs once she has laid the second or third egg.
- Full incubation typically doesn’t begin until most, if not all, of the eggs have been laid.
How Long Does It Take for Budgie Eggs to Hatch?
Once the incubation process begins, it generally takes 18 to 21 days for budgie eggs to hatch.
Some important points to note:
- The exact timing can vary depending on factors like temperature and humidity conditions.
- If an egg hasn’t hatched after 23 days, it’s likely infertile or the embryo has died.
How Can You Incubate Budgie Eggs at Home?
How Do You Choose the Right Incubator Machine for Budgie Eggs?
Selecting the right incubator machine is crucial for successful home incubation. Consider these factors:
- Capacity: Ensure it can accommodate the number of eggs you plan to incubate.
- Temperature Control: Look for precise temperature controls, as even small fluctuations can affect hatching success.
- Humidity Control: It should provide control over humidity levels.
- Automatic Turning: Some incubators automatically turn eggs, which is essential for even development.
What Is the Correct Incubator Temperature for Budgie Eggs?
For optimal development, the incubator temperature for budgie eggs should be maintained at approximately 37.5°C (99.5°F).
How Do You Adjust the Incubator Humidity for Budgie Eggs?
Proper humidity is essential. Aim for humidity levels of 40-50% for the first 18 days of incubation, increasing to 60-70% for the final days to assist in hatching.
Why Is It Important to Turn Eggs Regularly During Incubation?
Turning eggs regularly during incubation helps prevent the embryo from sticking to the shell and ensures even temperature distribution.
It’s important to note:
- Eggs should be turned at least 3-5 times daily.
- Most automatic incubators manage this, but manual turning might be required with some incubators.
What Are Some Alternative Methods for Incubating Budgie Eggs?
While using an incubator is the most reliable method, alternatives exist:
- Broody Budgie Hens: A broody hen will naturally incubate and hatch her eggs.
- Broody Hens of Other Bird Species: In some cases, broody hens of other species may be used to incubate and hatch budgie eggs.
V. Budgie Egg and Chick Care
This section aims to provide valuable insights into the intricate aspects of Budgie Egg and Chick Care.
It will explore that budgie owners often encounter, delving into critical topics from handling budgie eggs to managing a budgie’s diet during its egg-laying phase.
Can You Touch a Budgie’s Egg? If So, How Should You Do It?
You should employ the following steps when touching a budgie’s egg:
- Wash Your Hands: Always ensure your hands are clean and free of any lotions or scented products. This helps prevent the transmission of harmful bacteria to the egg also.
- Direct Contact: Avoid touching the eggs with bare hands, as oils and bacteria can harm the developing embryo inside. Use clean gloves or tissue for gentle handling.
- Be Gentle: Budgie eggs are delicate. Hold them gently to avoid causing any damage.
- Quick and Efficient: Make your interaction quick. This minimizes the time the eggs are away from the warm environment of the nest.
- Put back correct place: Make sure that the egg you take in your hand is put back in its correct place.
- Avoid Frequent Handling: The less you handle the eggs, the better. It reduces the risk of accidents and keeps the mother budgie stress-free.
How Can You Prevent Your Budgie from Laying Eggs?
- Light Exposure: Regulating light exposure, ensuring not more than 8-10 hours of light per day, can help manage a budgie’s laying cycle.
- Diet Management: A diet low in fats and high in calcium can help in controlling excessive egg laying.
- Environment Alterations: Modifying the budgie’s environment to make it less suitable for breeding can also deter egg laying.
Do Budgies Eat Their Own Eggs and Why?
- Stress Response: Budgies might eat their eggs under stressful conditions or when they sense danger to their nest.
- Nutrient Replenishment: Consuming eggs may help replenish nutrients lost during egg production.
- Unfertilized Eggs: Budgies may eat unfertilized eggs to prevent the decomposition process that could attract predators.
What Should Be the Diet for Egg-Laying Budgies?
- High Calcium Foods: Incorporate foods high in calcium, like broccoli and spinach, to support egg production.
- Protein Sources: Include protein-rich sources like boiled eggs and legumes to enhance their nutritional profile.
- Seed Mix: Ensure a well-balanced seed mix for energy and additional nutrients.
How Can You Safely Handle Budgie Eggs?
- Clean Hands or Gloves: Always handle the eggs with clean, dry hands or gloves to prevent the transfer of bacteria.
- Gentle Touch: Use a gentle touch to avoid causing any damage.
- Infrequent Handling: Minimize the frequency of handling to prevent stress on the bird and potential harm to the eggs.
How Can You Deal with Egg Binding Symptoms in Budgies?
- Spotting the Signs: Look for signs like restlessness, difficulty moving, and loss of appetite.
- Fluids for hydration: Make sure the budgie is not dehydrated.
- Veterinary Help: Seek immediate veterinary help if egg binding is suspected. It’s a serious condition and requires professional medical attention. May the vet performe an ovocentesis (archived).
- Warm Environment: Providing a warm environment may help in some cases, but professional help is crucial.
What Should You Do When Budgie Eggs Are Not Hatching?
- Incubation Time: Note that the incubation period for budgie eggs is around 18-21 days.
- Non-viable Eggs: If eggs don’t hatch within this period, they might be infertile or non-viable.
- Safe Removal: Unhatched eggs should be carefully removed from the cage to prevent decomposition and potential health risks to the budgies.
By paying heed to these factors and applying the tips shared, one can assure their budgies a safer and healthier egg-laying and hatching experience.
What Are the Nesting Habits of Budgies?
Budgies display fascinating nesting habits that are crucial to understand, whether you are an avid bird watcher or a caring budgie owner.
How Do Budgies Build Their Nests?
- Nest Site Selection: Budgies, particularly the females, are keen selectors of nest sites. They prefer enclosed spaces that offer protection from predators and environmental elements.
- Nest Building: Unlike many other bird species, budgies do not collect twigs and leaves to construct elaborate nests. Instead, they find suitable cavities in trees or nesting boxes, where the female lays her eggs directly on the wooden floor.
- Nest Arrangement: Female budgies often chew the wooden surface of the nest, creating a fine sawdust that provides additional warmth and cushioning for her eggs.
How Should You Inspect a Budgie’s Nest?
- Frequency: Avoid frequent interruptions which can stress the birds. A weekly check should suffice.
- Timing: Aim to inspect the nest when the budgies are least active, usually mid-afternoon.
- Method: Use a small torch or your phone’s flashlight to gently illuminate the nest. Avoid touching the eggs or chicks.
Remember, the aim of inspecting the nest is to ensure the health and safety of the budgie family, not to disrupt their natural behaviors.
What Are the Stages of Budgie Chick Development?
The life of a budgie chick can be summarized into three primary stages:
- Hatching
- Feathering
- Fledging
Each of these stages plays a critical role in the development of the chick into a healthy adult budgie.
What Is Feathering in Budgie Chicks?
Feathering is a stage where the chicks begin to develop feathers, replacing their initial coat of fluffy down.
Feathering in budgies typically begins around the second week after hatching.
How Does Feather Development Occur in Budgie Chicks?
- Pin Feathers: Initially, budgie chicks develop ‘pin feathers’. These look like tiny, thin quills poking through the chick’s skin.
- Feather Sheaths: As pin feathers grow, they are covered by a protective casing or sheath.
- Feather Unfurling: Once fully grown, the sheath disintegrates, and the mature feather unfurls.
This process repeats until the budgie chick has a full plumage, usually by the fifth week after hatching.
What Are the Growth Stages of Budgie Chicks?
Budgie chicks undergo significant changes during their growth stages:
- Hatching: After 18 days of incubation, the chick breaks free from its shell. At this stage, it is blind and almost featherless.
- Nestling (1-3 weeks): The chick begins to develop pin feathers and relies on its parents for warmth and nourishment.
- Feathering (2-5 weeks): This stage sees the development of the chick’s full plumage. Its eyes also open during this period.
- Fledging (4-6 weeks): The chick becomes increasingly active, venturing out of the nest and learning to fly.
- Weaning (6-8 weeks): The fledgling begins to eat independently, marking its transition into a juvenile budgie.
By understanding these stages, we can better provide for the needs of our budgie chicks at every step of their development.
Understanding and Using Dummy Eggs
As we delve deeper into the world of budgie care, a unique and often overlooked topic comes to the forefront: dummy eggs.
Used as a powerful tool by avian enthusiasts worldwide, these faux eggs can offer numerous benefits when properly implemented.
What Are Dummy Eggs for Budgies?
Dummy eggs, also known as false or artificial eggs, are non-fertile eggs used as substitutes in bird nests.
They’re also typically can be made of plastic or ceramic and designed to mimic the size, color, and weight of real budgie eggs.
How Do Dummy Eggs Help in Budgie Breeding?
When it comes to budgie breeding, dummy eggs offer several advantages:
- Prevent Overbreeding: By replacing real eggs with dummy eggs, you can control the number of chicks a pair of budgies raises at one time, thus preventing overbreeding.
- Encourage Incubation Behavior: If your budgie is reluctant to incubate her eggs, introducing dummy eggs can stimulate her instinctual incubation behavior.
How to Use Dummy Eggs for Budgies?
To leverage the benefits of dummy eggs, here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
- Observe Your Budgies: Make sure your budgie has laid her eggs and started the incubation process.
- Replace Real Eggs with Dummy Eggs: Carefully swap out the real eggs with dummy ones while your budgie is away from the nest.
- Monitor Your Budgie’s Behavior: Keep an eye out for any changes in your budgie’s behavior. She should continue to incubate the dummy eggs as if they were real.
How Can Dummy Eggs Prevent Overbreeding in Budgies?
The key lies in the budgie’s incubation cycle. Once the budgie starts incubating her eggs, she won’t lay more eggs until the current batch has ‘hatched’ (or after a period if the eggs are infertile).
Replacing real eggs with dummy eggs effectively pauses the cycle, limiting the number of offspring.
How Can Dummy Eggs Help in Managing Egg-Laying Issues in Budgies?
For budgies suffering from chronic egg-laying, a condition where the female budgie lays eggs continuously without a male partner, dummy eggs can:
- Discourage Continuous Egg Laying: Introducing dummy eggs can trick the budgie into believing she has already laid enough eggs, thus stopping further egg production.
- Provide a Resting Phase: This method allows the female budgie’s body to recover from the exhaustive process of laying eggs.
How Long Should You Leave Dummy Eggs in a Budgie’s Nest?
As a rule of thumb, dummy eggs should be left in the nest for about 18-21 days, the normal incubation period for budgie eggs.
This timeframe allows the budgie to fulfill her incubation instincts without causing unnecessary stress or hormonal imbalances.
By leveraging the power of dummy eggs, budgie owners can help regulate breeding, control egg-laying issues, and ensure a healthier and happier life for their feathered friends.
FAQs
Can Female Budgies Lay Eggs without Mating?
Interestingly, female budgies can indeed lay eggs without mating, just like chickens do.
However, these eggs are infertile and will not hatch into chicks. For a budgie egg to be fertile, it must be fertilized by a male.
How Does Embryonic Development Occur in Budgie Eggs?
The development of a budgie embryo is a fascinating process:
- Day 1: The egg is fertilized.
- Day 2-3: The embryo begins to form.
- Day 4-7: Essential organs start developing.
- Day 8-14: Rapid growth occurs, and the chick begins to resemble a bird.
- Day 18-21: The chick is fully formed and ready to hatch.
How Can You Determine the Age of a Budgie Egg?
Determining the age of a budgie Egg can be a complex task.
Generally, observing the development stages under controlled conditions and using a candling method can provide insights.
Monitoring the size, color, and embryonic movement are key factors in age determination.
How Do You Ensure the Proper Temperature for Budgie Eggs?
Ensuring the proper temperature for budgie Eggs is crucial for successful incubation.
The ideal temperature is around 99.5°F (37.5°C). Utilize an incubator with a thermostat or maintain a stable room temperature.
Regularly monitor the temperature, and make gradual adjustments if needed.
What Are the Ethical Considerations Regarding Budgie Breeding?
Ethical considerations in budgie breeding encompass providing a humane environment, avoiding overbreeding, and complying with local laws and regulations.
Responsible breeding involves considering the health and well-being of both the adult budgies and the chicks, and being prepared to care for them appropriately.
How Often Do Budgies Lay Eggs in a Year?
The frequency of egg-laying in budgies can vary significantly, primarily depending on the environmental conditions and their overall health.
On average, Budgies may have 2-3 breeding cycles per year, each resulting in a clutch of about 4-6 eggs.
How Can You Support the Health of Egg-Laying Budgies?
Supporting the health of egg-laying budgies requires a balanced diet rich in protein and calcium, a comfortable and safe nesting environment, and regular vet check-ups.
Providing budgies with a stress-free environment is also crucial to prevent health complications.
What Factors Can Affect the Fertility of Budgie Eggs?
Several factors can affect the fertility of budgie eggs, including genetic compatibility between the parents, their overall health, the quality of their diet, and environmental stressors.
It’s crucial to ensure optimal conditions for budgies during the breeding season to enhance egg fertility.
What Should You Do If a Budgie Abandons Its Eggs?
If a budgie abandons its eggs, it may be necessary to intervene.
You could use an incubator to maintain the eggs at the correct temperature.
Consult a vet or a bird specialist to understand the best practices in this scenario and to ensure the welfare of both the budgie and its eggs.
Can Budgies Lay Eggs in Captivity?
Yes, budgies can and do lay eggs in captivity. This is more likely if they are provided with a suitable environment and conditions that mimic their natural habitat, including a suitable nest box, a balanced diet, and a healthy mate.
Is it Normal for Budgies to Lay Infertile Eggs?
Yes, it is entirely normal for budgies to lay infertile eggs, especially when there is no male budgie present.
Female budgies can produce eggs without mating, similar to chickens, but these eggs will not hatch as they are infertile.
How Can You Prevent Overbreeding in Budgies?
Overbreeding can be managed by regulating the breeding environment. Limiting access to nesting boxes, altering light exposure to mimic non-breeding seasons, and using dummy eggs can all discourage excessive egg-laying.

